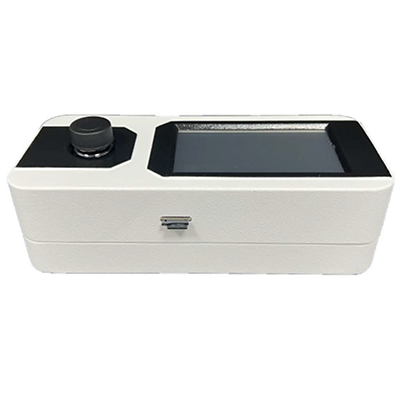
BOD rapid detector laboratory cabinet type
AMT/FY-BODBOD rapid measuring instrument, using microbial electrode method, can quickly determine the BOD value of water sample, and the operation is simple and accurate. At present, the measurement of BOD generally adopts the "five-day biochemical oxygen demand (B0D5) standard dilution method", the operation is more complicated, the technical requirements of the operator is high, and the time is long, which brings a lot of inconvenience to the sewage treatment and environmental detection. The time required for detecting a single sample is about 20 minutes, and it is widely applicable to the detection of BOD in surface water, groundwater, drinking water, pharmaceutical industry wastewater and industrial wastewater that does not contain obvious toxic effects on microorganisms. AMT/FXY-BOD type BOD rapid tester (hereinafter referred to as the instrument), using microbial electrode method, can quickly determine the BOD value of water samples, and easy to operate, accurate measurement. The time required for detecting a single sample is about 20 minutes, and it is widely used in the detection of BOD in surface water, groundwater, drinking water, pharmaceutical industry wastewater and industrial wastewater that does not contain obvious toxic effects on microorganisms. The method conforms to the "Rapid Determination of Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) in Water Quality by microbial Sensor" (Hchuan T86-2002), and is listed as A Class A method in the "Methods for Detection and Analysis of Water and Wastewater" (fourth edition) published in 2002.
The instrument adopts the microbial electrode method, and the microbial film is closely attached to the surface of the oxygen permeable film of the galvanic cell type dissolved oxygen electrode, that is, the microbial electrode is formed. The instrument adopts the flow measurement method, and the microbe membrane is fixed by the flow measurement pool assembly. Since the output signal value of the dissolved oxygen electrode is inversely proportional to the content of dissolved oxygen, when the liquid that does not contain any organic matter passes through the flow tank, the assimilation effect of microorganisms is very small, so the dissolved oxygen flowing through the microbial membrane is almost not reduced. When dissolved oxygen containing organic matter passes through the flow tank, the assimilation of the microorganisms becomes extremely active, consuming more dissolved oxygen, and resulting in less dissolved oxygen flowing through the microbial membrane. This change in the dissolved oxygen content directly causes the output of the dissolved oxygen electrode to change inversely, which proves that the change value of the output signal is inversely proportional to the content of organic matter in the sample, and thus the BOD value is calculated.